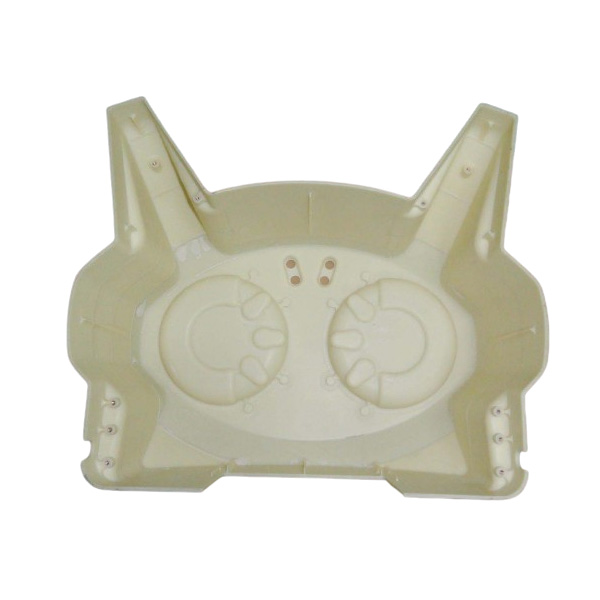
What Is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is an advanced manufacturing approach that utilizes cutting-edge technologies—such as 3D printing (SLA, SLM), CNC machining, and injection mold printing—to quickly transform digital 3D designs into functional, high-quality physical prototypes. These prototypes serve as critical tools for design validation, functional testing, and market evaluation before committing to full-scale production. By leveraging rapid prototyping, businesses can accelerate product development cycles, reduce costs associated with traditional tooling, and mitigate risks in the early stages of design.
Modern techniques like 3D printed injection molds and metal 3D printing (SLM) have further enhanced prototyping capabilities, enabling complex geometries, high precision, and material versatility. Whether for aerospace components, medical devices, or consumer products, rapid prototyping ensures faster iterations, improved design accuracy, and seamless transition to mass production.

Advantages of Rapid Prototyping in Product Development
1. Showcase Physical Models with High Accuracy
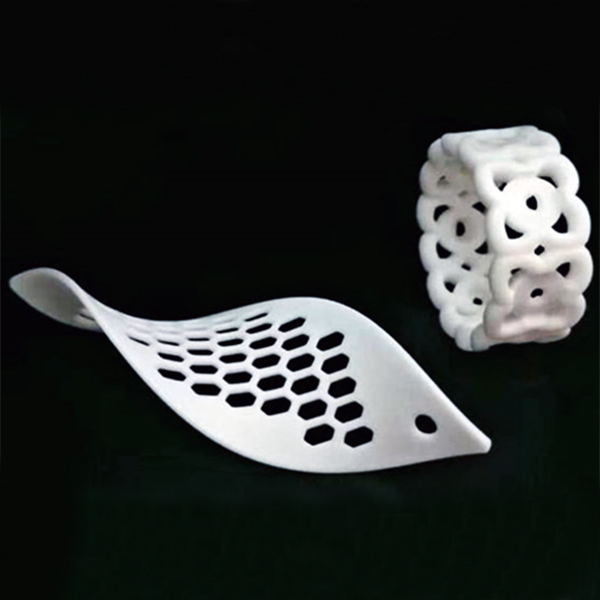
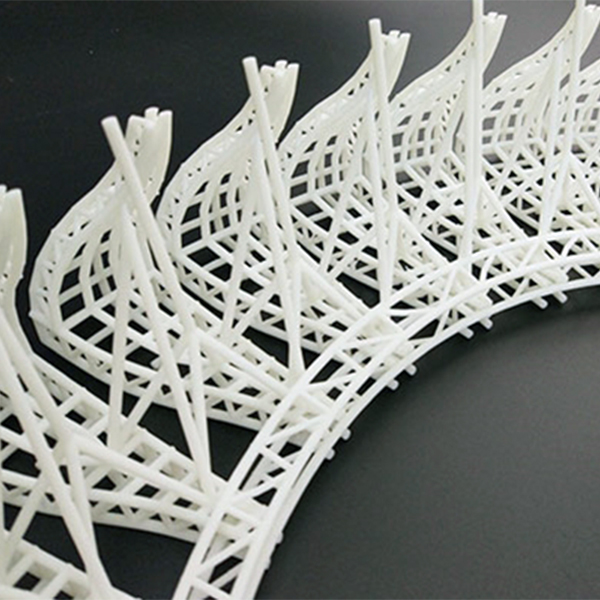
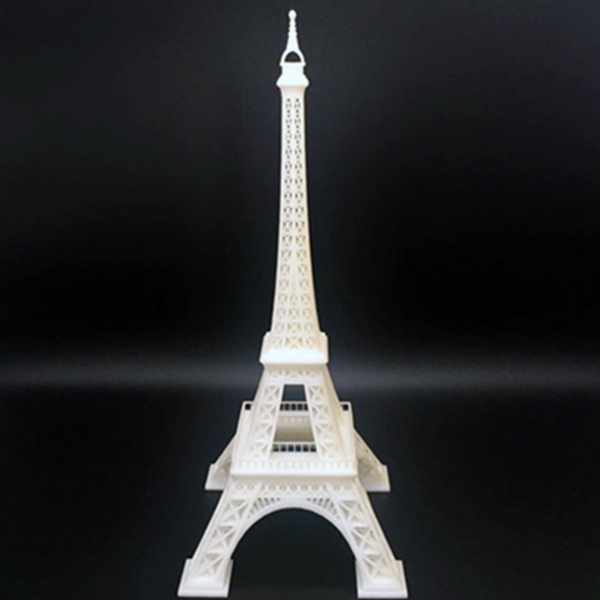
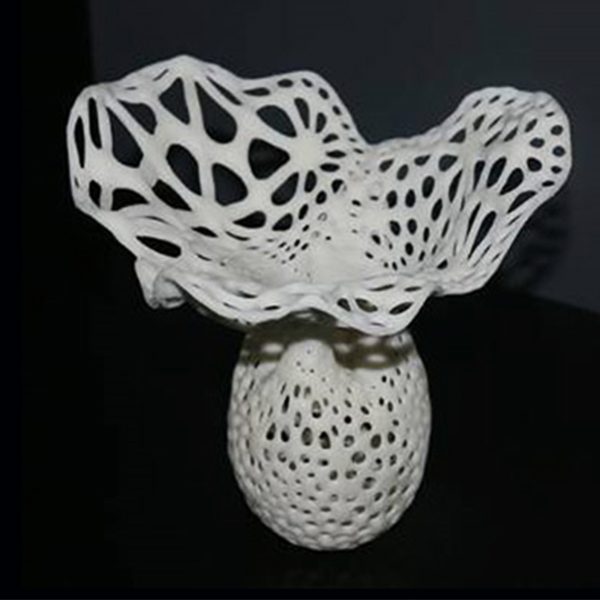
Rapid prototyping allows businesses to present tangible, fully functional models to stakeholders, investors, and potential customers. With SLA (Stereolithography) and SLM (Selective Laser Melting) 3D printing, even intricate designs with fine details—such as thin walls, internal channels, or textured surfaces—can be accurately replicated. This helps in securing funding, gathering feedback, and ensuring alignment with market expectations before final production.
2. Demonstrate Design Details Effectively
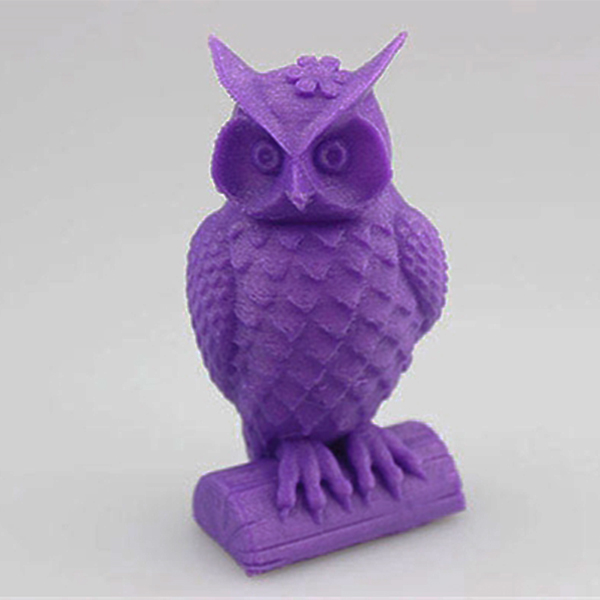
Prototypes provide a hands-on way to evaluate aesthetics, ergonomics, and functionality. Technologies like multi-material 3D printing and injection mold printing enable realistic surface finishes, color variations, and mechanical properties, closely mimicking the final product. This is especially useful for industries like automotive and consumer electronics, where visual and tactile appeal directly impact customer decisions.
3. Market Testing Without Heavy Investment
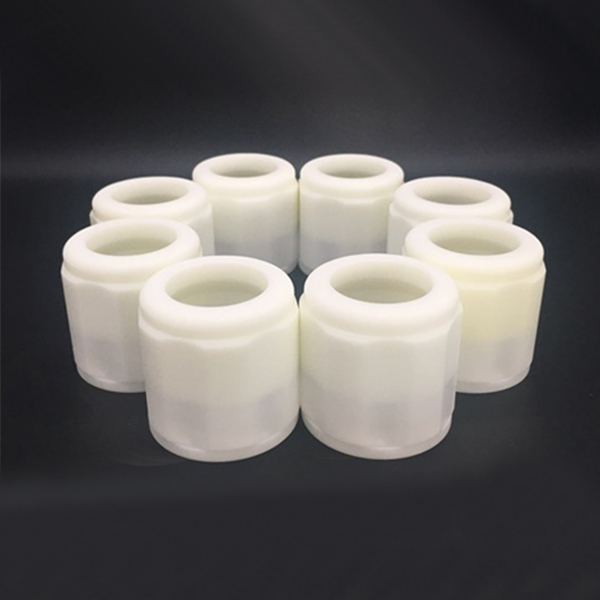
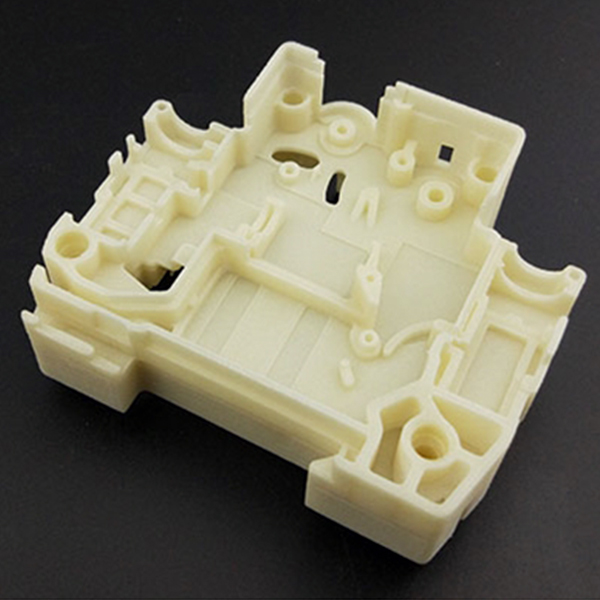
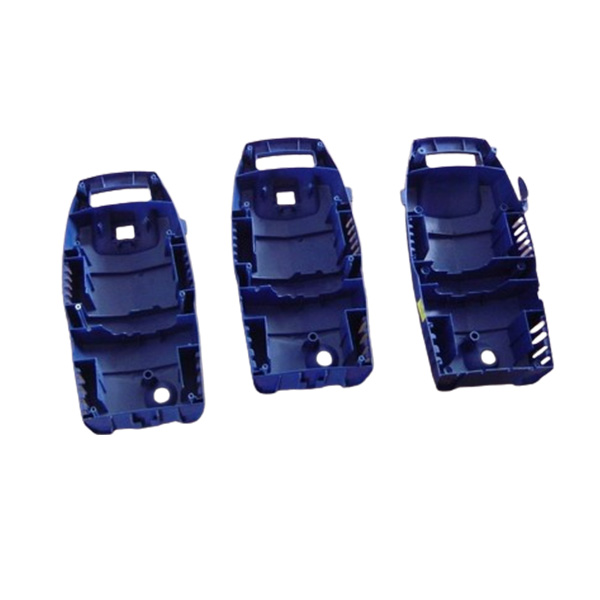
Instead of investing in expensive production tooling upfront, companies can use low-cost 3D printed prototypes to test market demand. For example, 3D printed injection molds allow small-batch production of functional parts, enabling real-world testing before committing to high-volume manufacturing. This reduces financial risks and ensures product-market fit.
4. Save Time & Costs by Identifying Flaws Early
Traditional manufacturing methods often lead to costly late-stage design changes. Rapid prototyping enables quick iterations, allowing engineers to detect and fix issues in geometry, fit, or performance early in the development cycle. SLA and SLM technologies ensure high precision, minimizing errors and reducing material waste.
5. Optimize Manufacturing Processes
Prototypes help refine production workflows by simulating real-world conditions. For instance, 3D printed injection molds can be used to test mold flow, cooling efficiency, and part ejection before investing in steel molds. This optimization leads to smoother mass production and higher-quality end products.
6. Explore Multiple Design Variations Efficiently
With rapid prototyping, businesses can experiment with different colors, materials, textures, and structural designs without expensive retooling. Multi-jet fusion (MJF) and SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) enable rapid production of diverse prototypes, facilitating A/B testing and customer preference analysis.
Conclusion
By integrating 3D printing (SLA, SLM), injection mold printing, and 3D printed tooling, rapid prototyping has become an indispensable strategy for modern product development. It bridges the gap between concept and reality, ensuring faster time-to-market, cost efficiency, and reduced risks. Whether for startups or established enterprises, adopting these technologies provides a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced industrial landscape.
Would you like insights on selecting the best rapid prototyping method for your project? Let us help you optimize your design-to-production journey!